The Sustainable Safety of Rijswijkseweg
By: Jenna Bilsback
In 1991 the Dutch adopted a traffic safety program where all new roads were designed to be sustainably safe. This methodology differed from the existing conditions because known safety principles were applied in the initial construction of the road, rather then after problems arose. During the design of new roads, five main sustainable safety principles are analyzed: functionality, homogeneity, forgiveness, recognition, and distinction of road status. Features are included to incorporate these concepts, and promote safe interactions between man, road, vehicle, and environment. Throughout the Netherlands roads can be studied, and their sustainable design features easily seen. Rijswijkseweg, a road in Den Haag, has many integrated sustainable safety features to protect the users of the road.
Figure 1. Is a locus map of Rijswijkseweg and its service roads.
Functionality:
Rijswijkseweg is a busy road which passes through Den Haag. The road provides connectivity between surrounding towns and many residential areas to the center of Den Haag. The primary purpose of Rijswijkseweg is distribution. The route works to efficiently move traffic between the previously mentioned areas. The road does this by including facilities for a large variety of through traffic, including cars, trams, and bikes.
For vehicular traffic, the road contains 2 lanes in each direction. This is rare road structure within the Netherlands because it allows for passing, and therefore facilitates speeding. Having a 2+2 lane road is beneficial as it reduces congestion, and allows for twice the amount of traffic to pass. In between the different directions of vehicular traffic is a pair of tram tracks. These two modes of transportation aim to cover the long portions of the road, quickly.
Rijswijkseweg is lined with a large amount of residences and a few local shops. As a result, the secondary function of the road is to provide access to these homes and businesses. In order to provide access, there are one way service roads on either side of the street.
Homogenity:
In order to ensure user safety, Rijswijkseweg aims to separate vehicles of different mass, speed, and direction. This was done by creating boundary conditions between the various modes of transportation.
In between the tram and the vehicular through traffic, there is a soft curb. This discourages cars from driving on the tram tracks, but is easily mountable by emergency vehicles. Along the right side of the vehicular through traffic is a line of parked cars. The parked cars provide a barrier between the rapidly moving cars and the slowly moving cars and bikes on the service roads. Traffic is not disturbed by parking cars because there is a passing lane in either direction. This is the major separation between the primary function (through traffic) and secondary functions (local access) of the route.
Next to the parked cars is small sidewalk which aims to further separate the primary and secondary functions of the road. On a few portions on the road, where there is extra space, there is an additional row of parking in between the small sidewalk boundary and the service road. The extra parking provides additional accessibility for residents and shoppers to their homes and the small businesses in the area. The larger separation also increases the safety of the users, so it is important to incorporate into sustainable designs where the layout permits. Finally, a large sidewalk provides pedestrians with easy access to the residences and businesses.There is a 3 inch curb separation the local cars and bikes from the foot traffic.
The photo below shows an average cross section of the road, and the separation of the different forms of transportation.
Figure 2. Is a typical cross section of Rijswijkseweg.
Forgiveness:
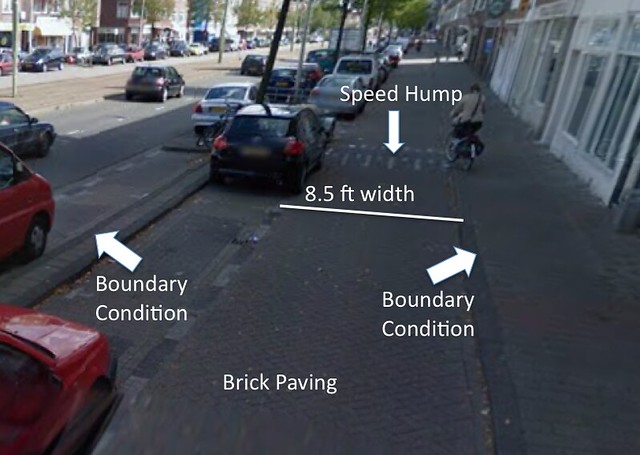
The design of any road has to make the target speed self enforcing because enforcement is unrealistic simply through signage. If traffic moves at targeted speeds, accidents have a lower risk of severe injury and causalities. All of the characteristics on the local access streets aim to reduce the speed of traffic, and therefore promote forgiveness in case of an accident. Some of the effective traffic calming measures include: brick pavement, lack of markings on the road, narrow lanes, no crosswalk, mixture of cycle and vehicular traffic, and speed humps. Many of these features creates a cozy atmosphere, which discourages speeding because it is a pleasant place to drive. A cross section of the service road is included below.
Figure 3. is a cross section of the service road that runs along Rijswijkseweg with several of the speed reducing features pointed out.
Recognition:
The service road is a specific road design that is seen all throughout the Netherlands. Roads that provide local access have specific characteristics that make them recognizable to their users throughout the nation. As a result of their recognizability, users automatically adjust their behavior according the their knowledge of the function. Many of the traffic calming measures mentioned above, including brick paving and the shared space of bikes and local access traffic, are key elements in an average Dutch service road.
Improved Sustainability:
In order to prevent through traffic from using the local access roads, the streets should be designed to keep through traffic out. On Rijswijkseweg, there are no measures to prevent this as the local access roads feed directly back into the through traffic just before the intersection. This promotes the mixture of functionality if there is a traffic jam on the through road. If through traffic utilizes the service roads, the sustainable safety of the service roads is compromised. One way to avoid through traffic from utilizing the service roads is to have the service road exit in an adjacent neighborhood, and not directly back onto the through lanes. Below you will see an image of the service road adjacent to Rijswijkseweg. The existing service road exit is displayed in the photo below.
Figure 4. Is a photo of the flow of the service road back into the main distributer lanes.